Responsible for creating and managing grammar items and performing checks on grammars. More...
#include <grammar_factory.hpp>
Classes | |
| struct | FactoryItem |
| Represents an individual grammar item with its associated symbol table. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| void | Init () |
| Initializes the GrammarFactory and populates the items vector with initial grammar items. | |
| Grammar | PickOne (int level) |
| Picks a random grammar based on the specified difficulty level (1, 2, or 3). | |
| Grammar | GenLL1Grammar (int level) |
| Generates a LL(1) random grammar based on the specified difficulty level. | |
| Grammar | GenSLR1Grammar (int level) |
| Generates a SLR(1) random grammar based on the specified difficulty lefel. | |
| Grammar | Lv1 () |
| Generates a Level 1 grammar. | |
| Grammar | Lv2 () |
| Generates a Level 2 grammar by combining Level 1 items. | |
| Grammar | Lv3 () |
| Generates a Level 3 grammar by combining a Level 2 item and a Level 1 item. | |
| Grammar | Lv4 () |
| Generates a Level 4 grammar by combining Level 3 and Level 1 items. | |
| Grammar | Lv5 () |
| Generates a Level 5 grammar by combining Level 4 and Level 1 items. | |
| Grammar | Lv6 () |
| Generates a Level 6 grammar by combining Level 5 and Level 1 items. | |
| Grammar | Lv7 () |
| Generates a Level 7 grammar by combining Level 6 and Level 1 items. | |
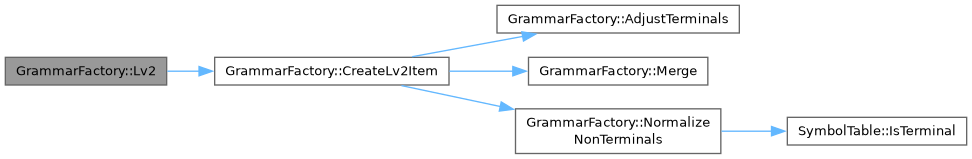
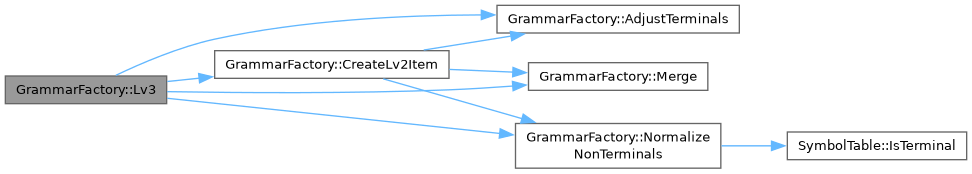
| FactoryItem | CreateLv2Item () |
| Creates a Level 2 grammar item for use in grammar generation. | |
| bool | HasUnreachableSymbols (Grammar &grammar) const |
| Checks if a grammar contains unreachable symbols (non-terminals that cannot be derived from the start symbol). | |
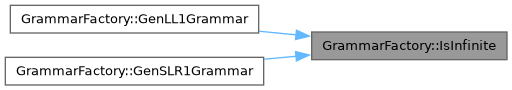
| bool | IsInfinite (Grammar &grammar) const |
| Checks if a grammar is infinite, meaning there are non-terminal symbols that can never derive a terminal string. This happens when a production leads to an infinite recursion or an endless derivation without reaching terminal symbols. For example, a production like: | |
| bool | HasDirectLeftRecursion (const Grammar &grammar) const |
| Checks if a grammar contains direct left recursion (a non-terminal can produce itself on the left side of a production in one step). | |
| bool | HasIndirectLeftRecursion (const Grammar &grammar) const |
| Checks if a grammar contains indirect left recursion. | |
| bool | HasCycle (const std::unordered_map< std::string, std::unordered_set< std::string > > &graph) const |
| Checks if directed graph has a cycle using topological sort. | |
| std::unordered_set< std::string > | NullableSymbols (const Grammar &grammar) const |
| Find nullable symbols in a grammar. | |
| void | RemoveLeftRecursion (Grammar &grammar) |
| Removes direct left recursion in a grammar. A grammar has direct left recursion when one of its productions is. | |
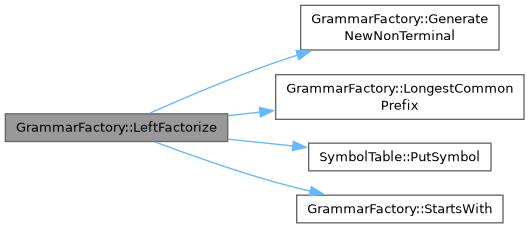
| void | LeftFactorize (Grammar &grammar) |
| Performs left factorization. A grammar can be left factorized if it has productions with the same prefix for one non-terminal. For example: | |
| std::vector< std::string > | LongestCommonPrefix (const std::vector< production > &productions) |
| Finds the longest common prefix among a set of productions. | |
| bool | StartsWith (const production &prod, const std::vector< std::string > &prefix) |
| Checks if a production starts with a given prefix. | |
| std::string | GenerateNewNonTerminal (Grammar &grammar, const std::string &base) |
| Generates a new non-terminal symbol that is unique in the grammar. | |
| void | NormalizeNonTerminals (FactoryItem &item, const std::string &nt) const |
| Replaces all non-terminal symbols in a grammar item with a single target non-terminal. | |
| void | AdjustTerminals (FactoryItem &base, const FactoryItem &cmb, const std::string &target_nt) const |
| Adjusts the terminal symbols between two grammar items. | |
| std::unordered_map< std::string, std::vector< production > > | Merge (const FactoryItem &base, const FactoryItem &cmb) const |
| Merges the grammar rules of two grammar items into a single grammar. | |
Public Attributes | |
| std::vector< FactoryItem > | items |
| A vector of FactoryItem objects representing different level 1 grammar items created by the Init method. | |
| std::vector< std::string > | terminal_alphabet_ |
| A vector of terminal symbols (alphabet) used in the grammar. | |
| std::vector< std::string > | non_terminal_alphabet_ |
| A vector of non-terminal symbols (alphabet) used in the grammar. | |
Detailed Description
Responsible for creating and managing grammar items and performing checks on grammars.
Member Function Documentation
◆ AdjustTerminals()
| void GrammarFactory::AdjustTerminals | ( | FactoryItem & | base, |
| const FactoryItem & | cmb, | ||
| const std::string & | target_nt ) const |
Adjusts the terminal symbols between two grammar items.
This function modifies the terminal symbols of a base grammar item so that they do not conflict with those of the item being combined. It also renames terminals to ensure consistency and inserts the target non-terminal where appropriate.
- Parameters
-
base The base grammar item to adjust. cmb The grammar item being combined with the base. target_nt The target non-terminal symbol used for replacement.
◆ CreateLv2Item()
| GrammarFactory::FactoryItem GrammarFactory::CreateLv2Item | ( | ) |
Creates a Level 2 grammar item for use in grammar generation.
This function generates a Level 2 grammar item, which can be used as a building block for creating more complex grammars.
- Returns
- A FactoryItem representing a Level 2 grammar.

◆ GenerateNewNonTerminal()
| std::string GrammarFactory::GenerateNewNonTerminal | ( | Grammar & | grammar, |
| const std::string & | base ) |
Generates a new non-terminal symbol that is unique in the grammar.
This function creates a new non-terminal symbol by appending a prime symbol (') to the base name until the resulting symbol is not already present in the grammar's symbol table. It is used during left factorization to introduce new non-terminals for factored productions.
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar in which the new non-terminal will be added. base The base name for the new non-terminal.
- Returns
- A unique non-terminal symbol derived from the base name.

◆ GenLL1Grammar()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::GenLL1Grammar | ( | int | level | ) |
Generates a LL(1) random grammar based on the specified difficulty level.
- Parameters
-
level The difficulty level (1, 2, or 3)
- Returns
- A random LL(1) grammar.
◆ GenSLR1Grammar()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::GenSLR1Grammar | ( | int | level | ) |
Generates a SLR(1) random grammar based on the specified difficulty lefel.
- Parameters
-
level The difficulty level (1, 2, or 3)
- Returns
- A random SLR(1) grammar.
◆ HasCycle()
| bool GrammarFactory::HasCycle | ( | const std::unordered_map< std::string, std::unordered_set< std::string > > & | graph | ) | const |
Checks if directed graph has a cycle using topological sort.
- Parameters
-
graph The directed graph.
- Returns
- true if grammar has cycle.
◆ HasDirectLeftRecursion()
| bool GrammarFactory::HasDirectLeftRecursion | ( | const Grammar & | grammar | ) | const |
Checks if a grammar contains direct left recursion (a non-terminal can produce itself on the left side of a production in one step).
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to check.
- Returns
- true if there is direct left recursion, false otherwise.

◆ HasIndirectLeftRecursion()
| bool GrammarFactory::HasIndirectLeftRecursion | ( | const Grammar & | grammar | ) | const |
Checks if a grammar contains indirect left recursion.
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to check.
- Returns
- true if there is direct left recursion, false otherwise.
◆ HasUnreachableSymbols()
| bool GrammarFactory::HasUnreachableSymbols | ( | Grammar & | grammar | ) | const |
Checks if a grammar contains unreachable symbols (non-terminals that cannot be derived from the start symbol).
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to check.
- Returns
- true if there are unreachable symbols, false otherwise.
◆ Init()
| void GrammarFactory::Init | ( | ) |
Initializes the GrammarFactory and populates the items vector with initial grammar items.
◆ IsInfinite()
| bool GrammarFactory::IsInfinite | ( | Grammar & | grammar | ) | const |
Checks if a grammar is infinite, meaning there are non-terminal symbols that can never derive a terminal string. This happens when a production leads to an infinite recursion or an endless derivation without reaching terminal symbols. For example, a production like:
could lead to an infinite derivation of non-terminals.
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to check.
- Returns
- true if the grammar has infinite derivations, false otherwise.

◆ LeftFactorize()
| void GrammarFactory::LeftFactorize | ( | Grammar & | grammar | ) |
Performs left factorization. A grammar can be left factorized if it has productions with the same prefix for one non-terminal. For example:
could be left factorized because it has "a" as the common prefix. The left factorization is done by adding a new non-terminal symbol that contains the uncommon part, and by unifying the common prefix in one production. So:
would become:
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to be left factorized.

◆ LongestCommonPrefix()
| std::vector< std::string > GrammarFactory::LongestCommonPrefix | ( | const std::vector< production > & | productions | ) |
Finds the longest common prefix among a set of productions.
This function computes the longest sequence of symbols that is common to the beginning of all productions in the given vector. It is used during left factorization to identify common prefixes that can be factored out.
- Parameters
-
productions A vector of productions to analyze.
- Returns
- A vector of strings representing the longest common prefix. If no common prefix exists, an empty vector is returned.

◆ Lv1()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv1 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 1 grammar.
- Returns
- A Level 1 grammar.

◆ Lv2()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv2 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 2 grammar by combining Level 1 items.
- Returns
- A Level 2 grammar.

◆ Lv3()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv3 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 3 grammar by combining a Level 2 item and a Level 1 item.
- Returns
- A Level 3 grammar.
◆ Lv4()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv4 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 4 grammar by combining Level 3 and Level 1 items.
This function creates a more complex grammar by combining elements from Level 3 and Level 1 grammars. It is used to generate grammars with increased complexity for testing or parsing purposes.
- Returns
- A Level 4 grammar.
◆ Lv5()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv5 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 5 grammar by combining Level 4 and Level 1 items.
This function creates a more advanced grammar by combining elements from Level 4 and Level 1 grammars. It is used to generate grammars with higher complexity for testing or parsing purposes.
- Returns
- A Level 5 grammar.
◆ Lv6()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv6 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 6 grammar by combining Level 5 and Level 1 items.
This function creates a highly complex grammar by combining elements from Level 5 and Level 1 grammars. It is used to generate grammars with advanced structures for testing or parsing purposes.
- Returns
- A Level 6 grammar.

◆ Lv7()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::Lv7 | ( | ) |
Generates a Level 7 grammar by combining Level 6 and Level 1 items.
This function creates a very complex grammar by combining elements from Level 6 and Level 1 grammars. It is used to generate grammars with highly advanced structures for testing or parsing purposes.
- Returns
- A Level 7 grammar.

◆ Merge()
| std::unordered_map< std::string, std::vector< production > > GrammarFactory::Merge | ( | const FactoryItem & | base, |
| const FactoryItem & | cmb ) const |
Merges the grammar rules of two grammar items into a single grammar.
This function performs a raw combination of the production rules from both grammar items, resulting in a single grammar map that contains all productions.
- Parameters
-
base The first grammar item. cmb The second grammar item.
- Returns
- A merged grammar map containing all production rules from both inputs.
◆ NormalizeNonTerminals()
| void GrammarFactory::NormalizeNonTerminals | ( | FactoryItem & | item, |
| const std::string & | nt ) const |
Replaces all non-terminal symbols in a grammar item with a single target non-terminal.
This function is used during grammar combination to normalize the non-terminal symbols in a given FactoryItem, so that they are consistent and compatible with another item.
- Parameters
-
item The grammar item whose non-terminals will be renamed. nt The new non-terminal symbol that will replace all existing ones.
◆ NullableSymbols()
| std::unordered_set< std::string > GrammarFactory::NullableSymbols | ( | const Grammar & | grammar | ) | const |
Find nullable symbols in a grammar.
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to check.
- Returns
- set of nullable symbols.
◆ PickOne()
| Grammar GrammarFactory::PickOne | ( | int | level | ) |
Picks a random grammar based on the specified difficulty level (1, 2, or 3).
- Parameters
-
level The difficulty level (1, 2, or 3).
- Returns
- A randomly picked grammar.
◆ RemoveLeftRecursion()
| void GrammarFactory::RemoveLeftRecursion | ( | Grammar & | grammar | ) |
Removes direct left recursion in a grammar. A grammar has direct left recursion when one of its productions is.
where A is a non-terminal symbol and "a" the rest of the production. The procedure removes direct left recursion by adding a new non-terminal. So, if the productions with left recursion are:
the result would be:
- Parameters
-
grammar The grammar to remove left recursion.
◆ StartsWith()
| bool GrammarFactory::StartsWith | ( | const production & | prod, |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | prefix ) |
Checks if a production starts with a given prefix.
This function determines whether the symbols in a production match the provided prefix sequence at the beginning. It is used during left factorization to identify productions that share a common prefix.
- Parameters
-
prod The production to check. prefix The sequence of symbols to compare against the beginning of the production.
- Returns
- true if the production starts with the prefix, false otherwise.

Member Data Documentation
◆ items
| std::vector<FactoryItem> GrammarFactory::items |
A vector of FactoryItem objects representing different level 1 grammar items created by the Init method.
◆ non_terminal_alphabet_
| std::vector<std::string> GrammarFactory::non_terminal_alphabet_ |
A vector of non-terminal symbols (alphabet) used in the grammar.
◆ terminal_alphabet_
| std::vector<std::string> GrammarFactory::terminal_alphabet_ |
A vector of terminal symbols (alphabet) used in the grammar.
The documentation for this struct was generated from the following files:
- backend/grammar_factory.hpp
- backend/grammar_factory.cpp